Map services are fundamental elements of a modern Web GIS architecture. The role of the map services are to provide geospatial content by the standardized interface technologies. On this blog post I will cover the basic principles of the common map service types such as WMS, WMTS, WFS, Tiled Map etc.
The map service is a special service type that is optimized for the geospatial content. In generally, the map services may be equated to the ordinary service interfaces such as WebServices and REST. The map services can be roughly divided into three main categories: 1) Feature/vector based services, 2) Image based services and 3) Tiled image services.
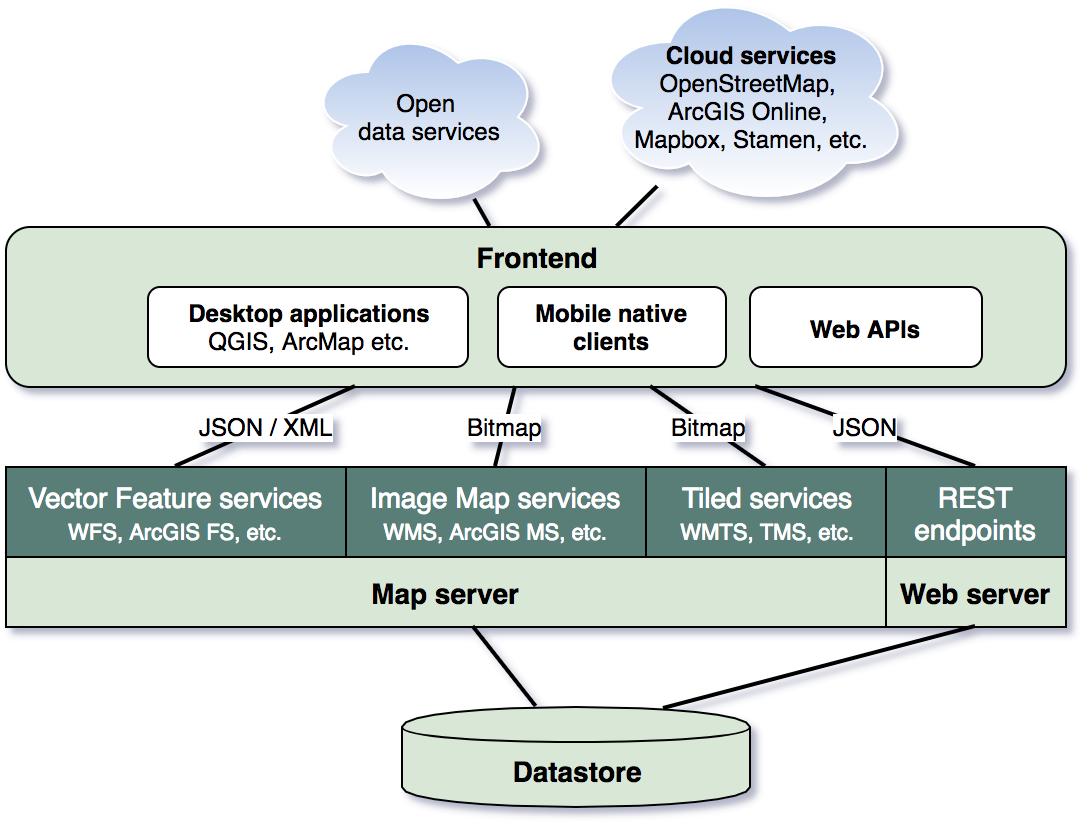 Elements of a typical Web GIS architecture.
Elements of a typical Web GIS architecture.
List of the Terms
- GIS: Geographic Information System
- Map service: a web interface that provides geospatial content
- Tiled map: a map displayed in a browser by seamlessly joining dozens of individually requested image files over the internet Wikipedia
- Map server: a server environment to provide geospatial web interfaces
- Basemap layer: a bottom layer of the map - f.ex. a streetmap, satellite images, etc.
- Operational layers: all kinds of business data on a basemap - f.ex. observations, sensor feeds, query or geoprocessing results etc.
1. Feature based services
The feature based services are probably the most common technology that is used to provide an operational map content. The feature services are used for all kind of the vector formatted data such as points on map, analysis results, boundaries etc. Characteristic for the feature services is a text (=feature) based data format such as GeoJSON, JSON or XML. The service types are for example, WFS and ArcGIS FeatureService.
 This picture represents 15 minutes drive-time area from the Solita office in Helsinki. In addition, the number of inhabitants in the area has been calculated. This is a good example of using feature based data for the geospatial analysis. I created this analysis by using the population grid data provided the HSY and drive-time area calculation. Analysis is created by the Esri ArcGIS Online services.
This picture represents 15 minutes drive-time area from the Solita office in Helsinki. In addition, the number of inhabitants in the area has been calculated. This is a good example of using feature based data for the geospatial analysis. I created this analysis by using the population grid data provided the HSY and drive-time area calculation. Analysis is created by the Esri ArcGIS Online services.
Technical Overview
When using the feature services, the client is responsible to generate and draw the map based on the data coming from the backend. This approach will pass the main computing load of the map drawing to the client.
The feature service architecture allows the client to get full control to the geometrical objects and data can be stylized and modified freely without making backend calls. This is one of the key advantages of this approach. On the other hand, visualizing causes a computing load for the client that could be a problem when displaying high amount of features at once.
It is good to note that security may be a risk with the feature based services. In fact, the geospatial data is transferred as a clear text format over the network. Because of this, the actual coordinates can be easily read by using the standard web developer tools. It is recommended to use image based services if the security causes an issue.
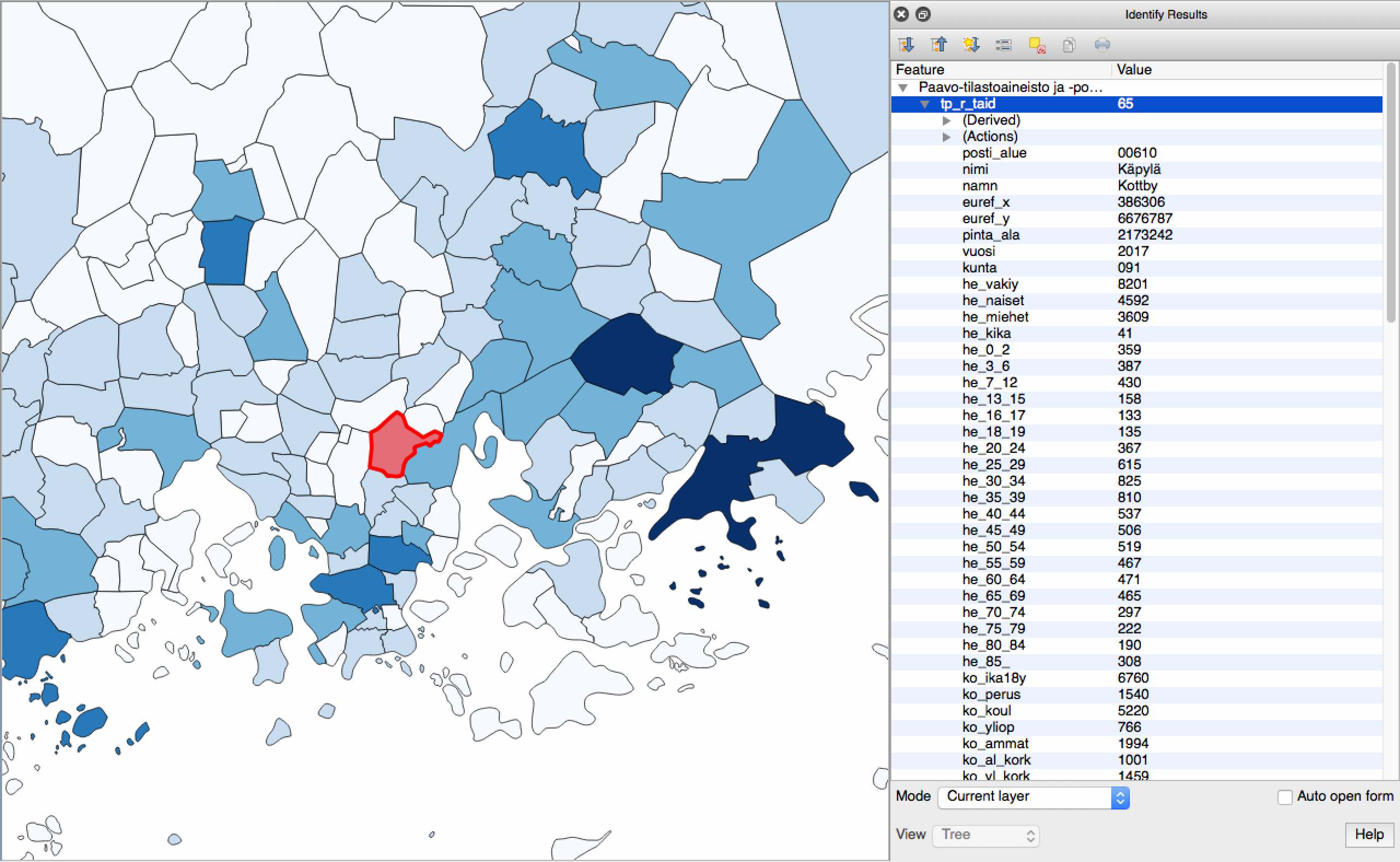 This picture represents the postcode boundaries colored by the population attribute. This is a common use case of the feature data. I created this example by QGIS.
This picture represents the postcode boundaries colored by the population attribute. This is a common use case of the feature data. I created this example by QGIS.
Simple feature service is a REST interface that returns a geospatial content as a GeoJSON string. That kind of the service is easy to implement with the standard web development tools.
The example below presents a typical response of the feature service. The response is a simple GeoJSON formatted string that contains one polygon geometry with attribute values. The table of coordinates represents corner vertexes of the polygon. The common WGS84 coordinate system (lat lon) is used. The Web APIs are typically capable of draw this kind of GeoJSON features on the map.
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[24.0256, 60.542],
[24.0732, 60.0481],
[25.1384, 59.9409],
[25.6263, 60.0897],
[25.6442, 60.4468],
[24.0256, 60.542]
]
]
},
"properties": {
"rowid": 2,
"name": "Sample polygon"
}
}
}
]
}
Realtime data by WebSockets
One useful application for the feature data is a WebSocket technology. The WebSocket can be used to stream JSON formatted data over the network. The WebSocket protocol provides high performance option to represent all kinds of the rapidly changing content.
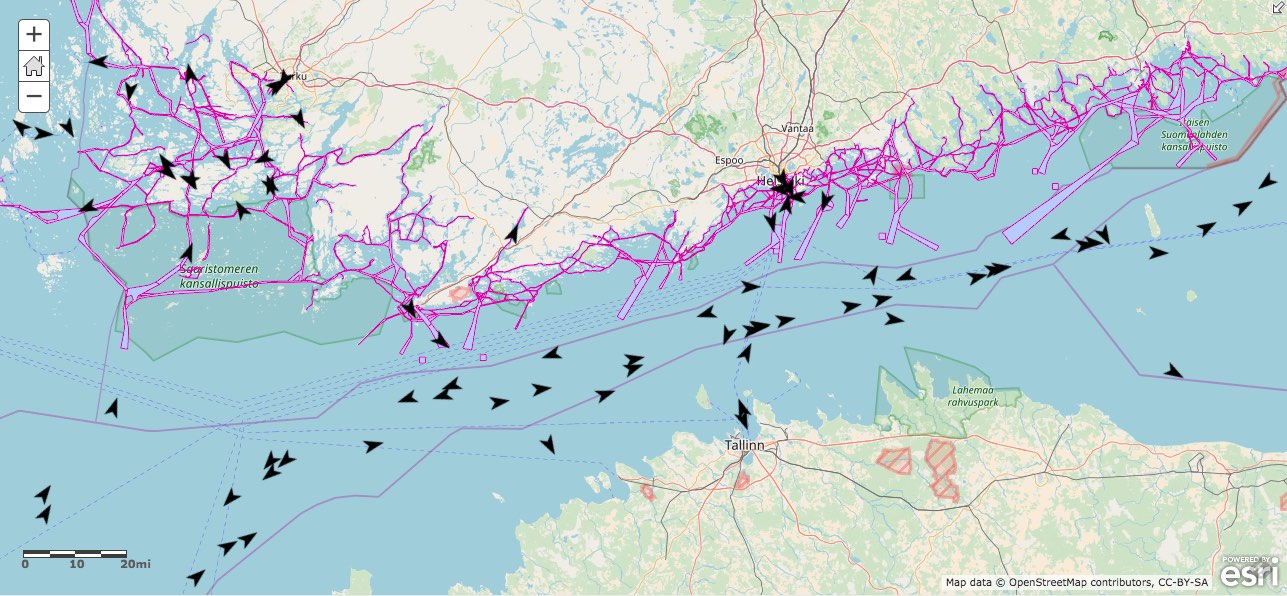 On this picture the marine traffic AIS data is streamed from the Liikennevirasto (Finnish Transport Agency) open data service as a WebSocket stream. The map is done by the Esri ArcGIS Online map viewer.
On this picture the marine traffic AIS data is streamed from the Liikennevirasto (Finnish Transport Agency) open data service as a WebSocket stream. The map is done by the Esri ArcGIS Online map viewer.
Feature based service types
- WFS - Web Feature Service Wikipedia
- ArcGIS FeatureService Esri documentation
Data types
- GeoJSON Wikipedia
- GeoRSS Wikipedia
- GML Wikkipedia
Vector based file formats
- Shapefile Wikipedia EsriWhitePaper
- KML Wikipedia
2. Image based Web Map Services
The image based web map services are typical service types provided by the map servers. The service types are for example, WMS and ArcGIS MapService. The image based map services are capable of handle complex datasets and for that reason this service type is often chosen when the data format is not suitable for the feature based services.
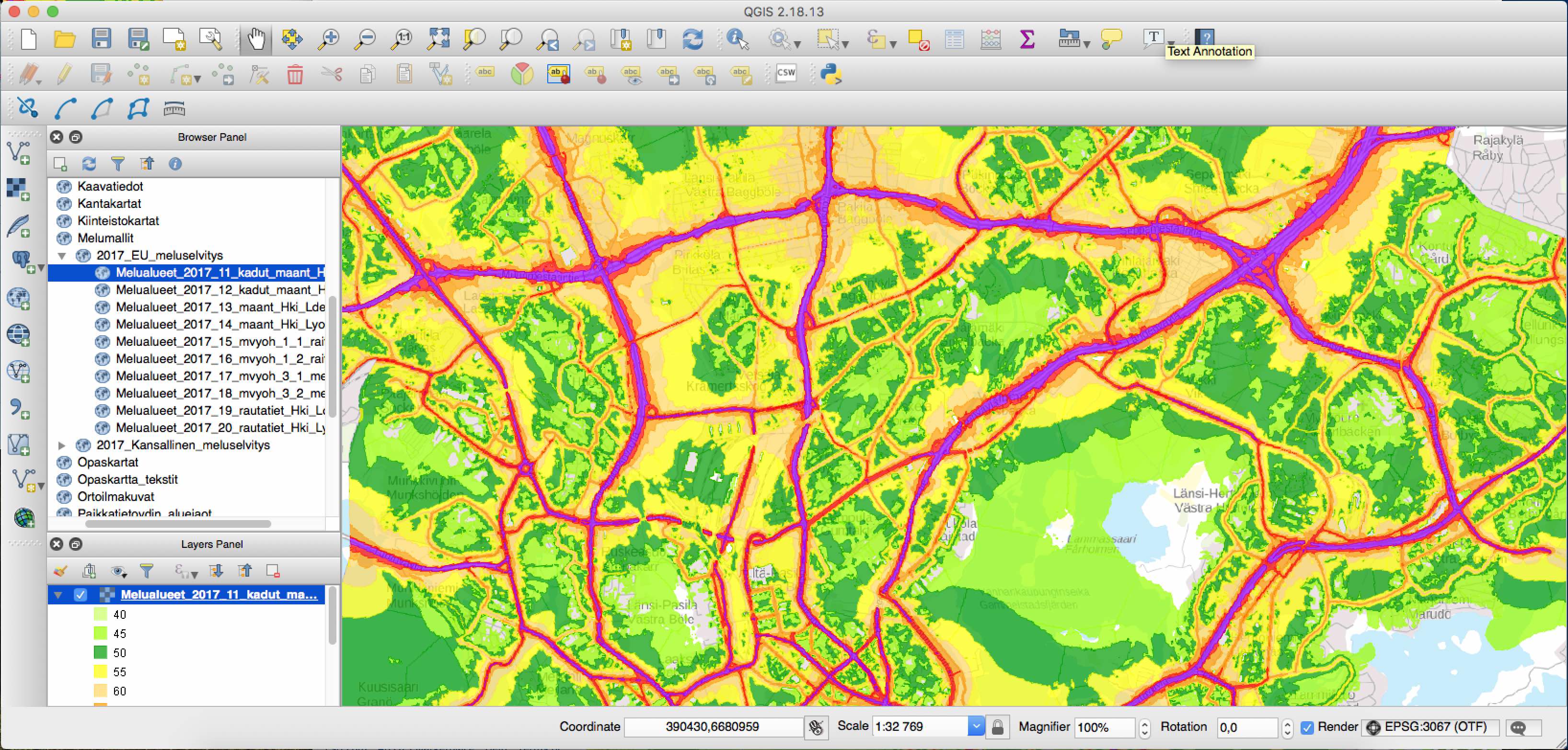 The city of Helsinki provides a wide set of open data through the map server. This picture presents the noise zones of the Helsinki region. The service is provided as a WMS interface.
The city of Helsinki provides a wide set of open data through the map server. This picture presents the noise zones of the Helsinki region. The service is provided as a WMS interface.
Technical Overview
From a technical point of view the data transfer format is main difference between the web map services and the feature based services. The web map services transfers the data by using bitmap formats such as JPG, PNG etc. From the architectural side the map server is responsible for generating the map images which are displayed by the client. The client don’t have an access to the geometrical objects.
It is notable that typically the map server generates a new result image every time when the request arrives to the web map service - practically when the map is moved on the screen. Often this also includes calls to the backend data such as the SQL geodatabase or filesystem. Caching is difficult since typically the every request generates a different result image. For that reason it is important to make sure that the services are well optimized.
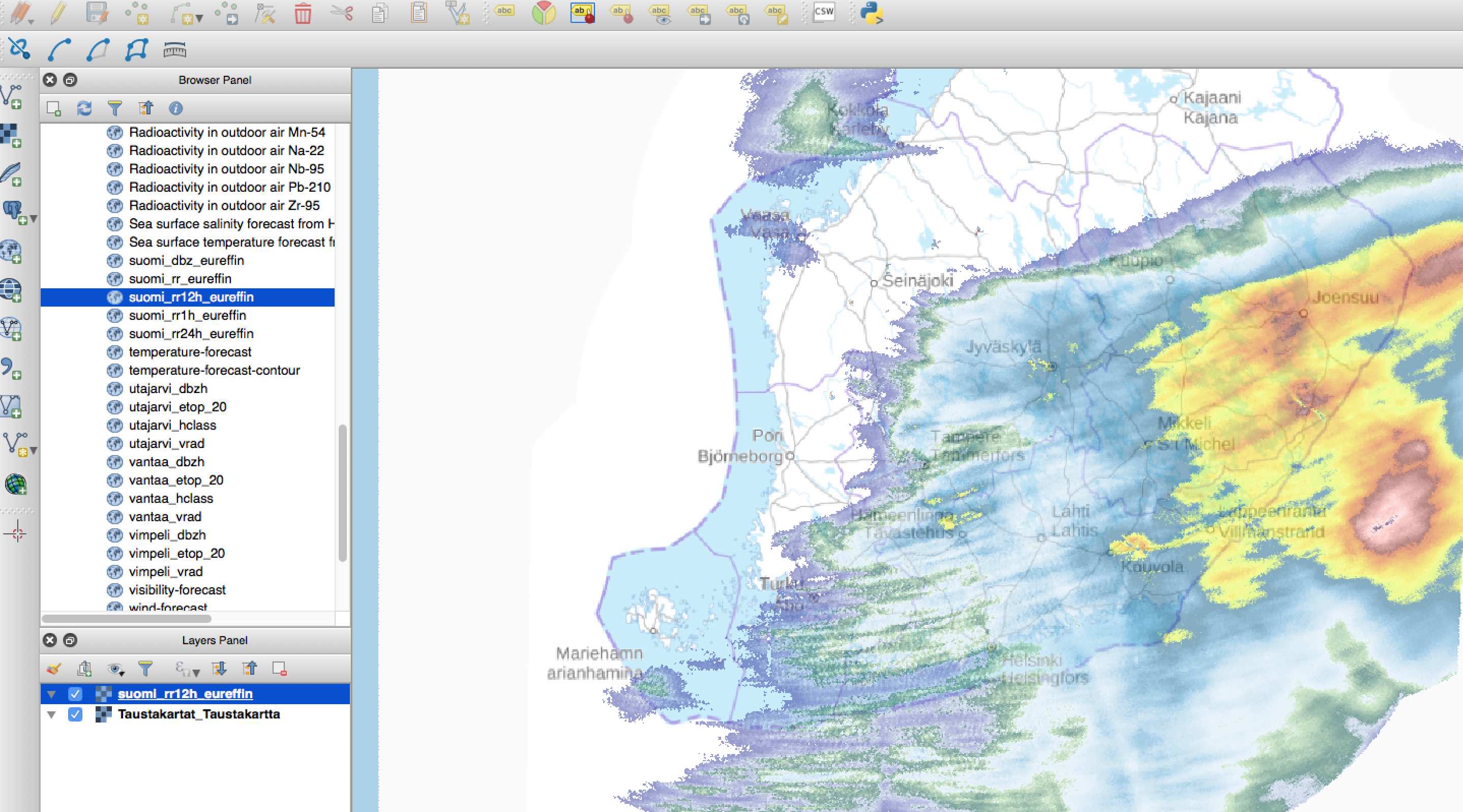 Finnish Meteorological Institute provides nice open data sets related to the weather. This example presents a real-time rain radar picture that is requested over the WMS service. The radar picture is a separate WMS layer that is put on the basemap. Picture is created by QGIS.
Finnish Meteorological Institute provides nice open data sets related to the weather. This example presents a real-time rain radar picture that is requested over the WMS service. The radar picture is a separate WMS layer that is put on the basemap. Picture is created by QGIS.
Web Map Service types
- WMS - Web Map Service Wikipedia
- ArcGIS MapService Esri documentation
3. Tiled Map Service
Background basemaps are typical use case for the tiled services. Tiled service is a common term for the map service that provides content by the fixed size image tiles. The tiled service types are for example, TMS (Tiled Map Service), WMTS (Web Map Tile Service) and ArcGIS Tiled service. Characteristic of the tiled services is the ability to handle high amount of image data with reasonable computing power. The data is typically static and preprocessed. Typical examples are satellite images, high detailed street maps, terrain maps etc.
 Source: Bing Maps Tile System
Source: Bing Maps Tile System
Technical Overview
Background data of the tiled services consists of map tiles. Collection of the tiles is called by tile cache. The map tiles are fixed size of image blocks, for example 256x256 pixels. The tile cache contains tiles for every zoom level from the map area. The disk usage of the cache can be extremely high. For example size of the detailed Finnish orthophoto basemap is almost 4TB! Kapsi
 Maanmittauslaitos peruskartta
Maanmittauslaitos peruskartta
The standard that defines the tile size, numbering and available zoom levels is called by tiling scheme. The most common tiling scheme is supricely the Google scheme that is used in the WebMercator maps. The national basemaps such as the ETRS-TM35FIN maps has they own tiling scheme.
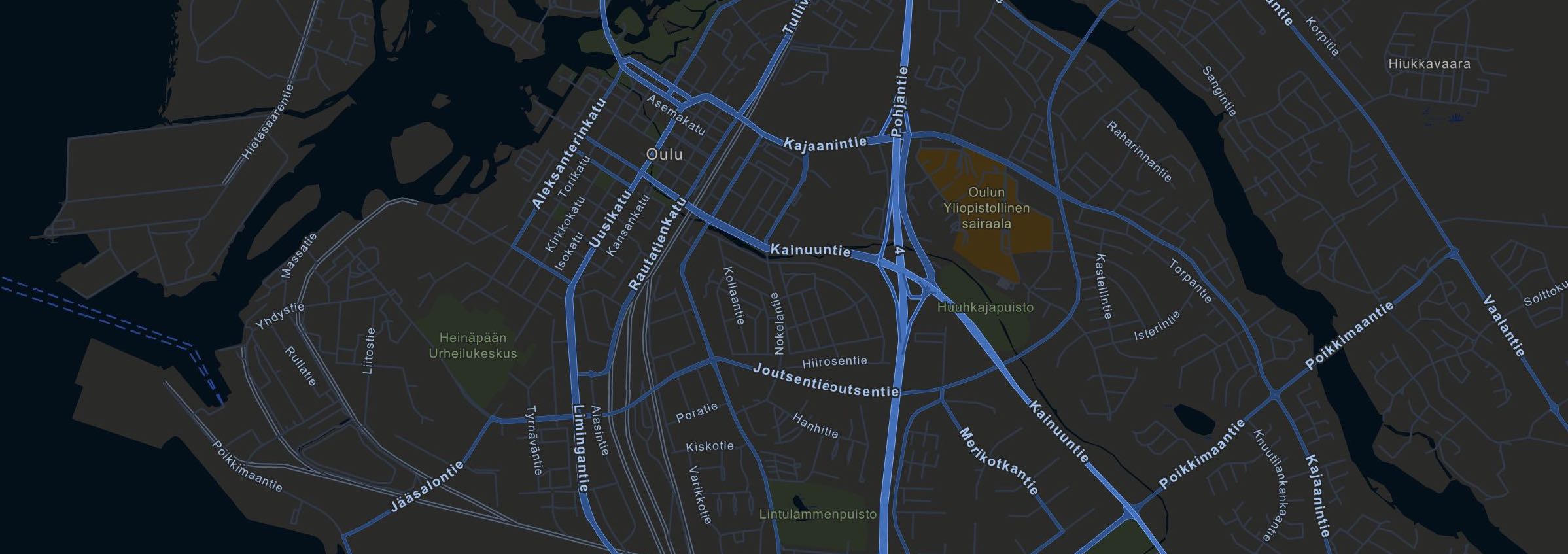 ArcGIS Streets Night
ArcGIS Streets Night
Running a Tile service
Running the tiled service is efficient since real time data processing is not required. The tile cache is calculated before the service is published so there is no image processing while the service is running. That allows the service handle high amount of data with a reasonable computing power. In the other hand, high computing power is required for creation of the tile cache and calculation can take easily few days with a standard desktop machine.
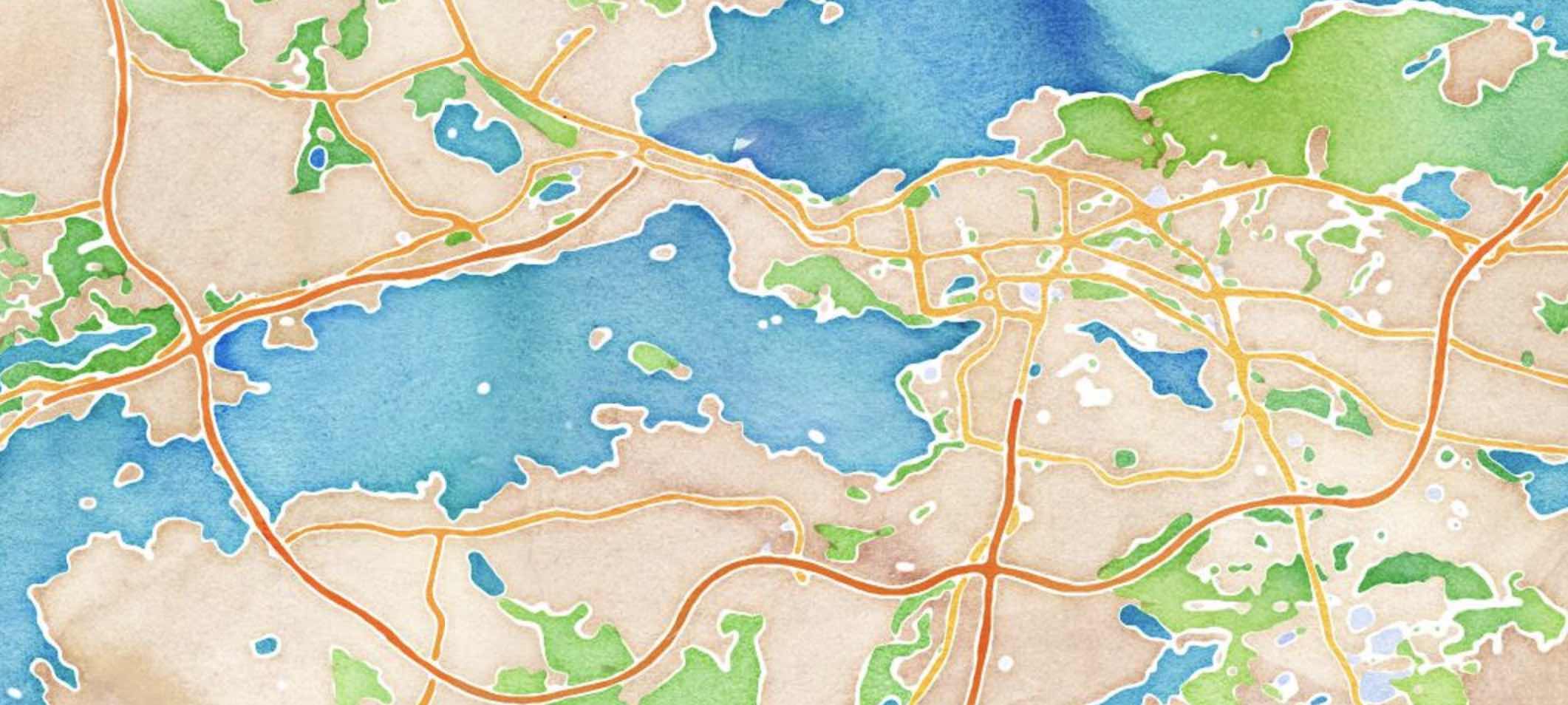 Stamen Watercolor
Stamen Watercolor
Vector Tiled Service
Latest innovation is so called vector tiled service. The vector tiled services are visually similar than the ordinary tiled services but instead of transferring bitmap tiles, the vector service is based to the vector tiles. The vector tiles are pre-calculated packages published to the map server. The Google is probably the most popular map service using the Vector Tiles.
Key advantages of the vector tiles compared to the ordinary image tiles are much smaller disc size and ability to change the map style and content on fly. Especially styling is handy since it opens opportunity to create the custom colored maps based on customer requirements.
The vector tiled service is suitable choice when the background map can represented by the vector objects.
Tiled Service types
Summary
The feature service is a suitable choice when the data amount is reasonable and geometrical content is simple points, lines and polygons. The feature service runs by a light backend solution and it does not necessary need a map server software.
The web map service (WMS) is a suitable option when the data is too complex and large to handle by the features/vectors. In addition, the image based WMS is a secure choice if the coordinate numbers should be hidden for the client.
The tiled services are useful for the static and large datasets such as satellite images and street maps. The tiled services can also used for the operational data layers if data is complex and performance requirement is high.
